Understanding Morse Code Components – Morse code, a system that revolutionized communication in the 19th century, continues to be a crucial tool in various fields today. Its simplicity, combined with the efficiency of transmitting information across long distances, makes Morse code a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and professionals alike. In this article, we will delve deeply into the components of Morse code, exploring its structure, uses, and enduring significance.
The Fundamental Elements of Morse Code
At its core, Morse code is a method of encoding textual information using sequences of two basic signal types: dots and dashes. These signals, also known as “dits” and “dahs,” are combined in various patterns to represent the letters of the alphabet, numerals, and punctuation marks. Let’s break down these elements in detail.
Dots and Dashes: The Building Blocks
- Dots (●):
Dots, or “dits,” are the shorter signals in Morse code. They are the basic unit of timing, with a standard duration that serves as the reference point for all other signals. - Dashes (▬):
Dashes, or “dahs,” are three times longer than dots. This distinction in length is critical, as it allows the receiver to differentiate between dots and dashes, ensuring accurate message interpretation.
Intra-character Spacing: Structure Within Characters
Each Morse code character is made up of a combination of dots and dashes. The space between these dots and dashes within the same character is referred to as intra-character spacing. This spacing is equivalent to the duration of one dot and is vital for maintaining the clarity of the transmitted message.
Inter-character Spacing: Separating Characters
The space between different characters is known as inter-character spacing. This pause is equal to the length of three dots and serves as a separator between the Morse code representations of individual letters or numerals. Without this spacing, Morse code messages would become a continuous stream of signals, leading to potential misinterpretations.
Inter-word Spacing: The Importance of Word Separation
When transmitting entire sentences or phrases, words must be clearly distinguished from one another. Inter-word spacing is the gap between words in Morse code, typically equivalent to the duration of seven dots. This extended pause is essential for maintaining the readability and coherence of the message.
Morse Code Timing and Rhythm: The Key to Accurate Transmission
The accuracy of Morse code transmission relies heavily on the timing and rhythm of the signals. Each component—dots, dashes, and the various types of spacing—must adhere to a precise timing structure to ensure that the receiver deciphers the message correctly. The rhythm of Morse code is almost musical, with its unique cadence forming the foundation of effective communication.
Timing Standards in Morse Code
The duration of a dot is the basic unit of time in Morse code, often referred to as a “time unit” or “T.” A dash, being three times longer, is defined as 3T. The intra-character space is 1T, the inter-character space is 3T, and the inter-word space is 7T. This systematic approach to timing ensures that Morse code can be transmitted accurately, even in challenging conditions.
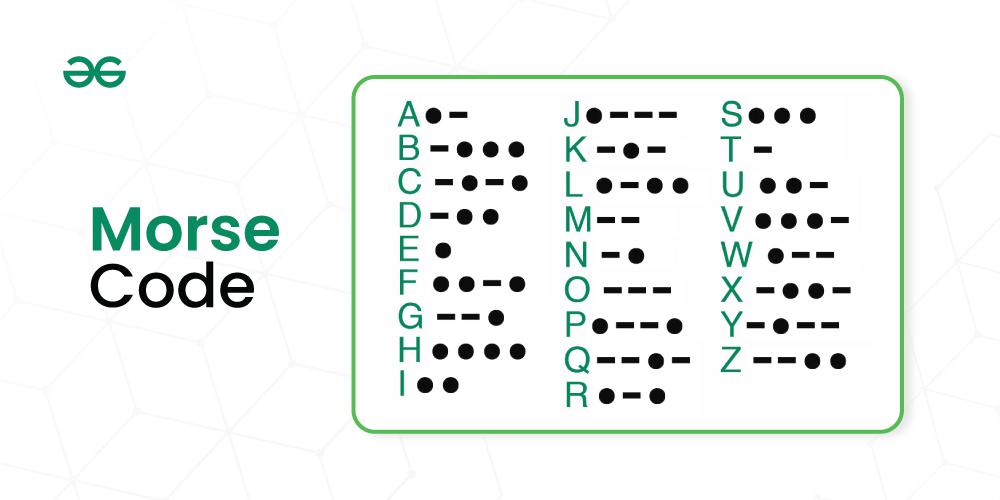
The Alphabet and Numbers in Morse Code
Morse code covers all 26 letters of the English alphabet, each represented by a unique combination of dots and dashes. For example:
- A is represented as ● ▬
- B is ▬ ● ● ●
- C is ▬ ● ▬ ●
Numbers are also included in Morse code, with each numeral having its own distinct pattern:
- 1 is ● ▬ ▬ ▬ ▬
- 2 is ● ● ▬ ▬ ▬
- 3 is ● ● ● ▬ ▬
Punctuation marks and special characters are also encoded in Morse code, though they are used less frequently than letters and numbers.
Applications of Morse Code: Past and Present
Historically, Morse code was vital in maritime communication, military operations, and early aviation. Its ability to transmit messages over telegraph wires and radio waves made it an indispensable tool. Even with the advent of modern digital communication, Morse code remains relevant in certain areas.
Modern Uses of Morse Code
- Amateur Radio:
Morse code, or CW (Continuous Wave), is still popular among amateur radio enthusiasts. It is prized for its simplicity and reliability, especially in low-signal conditions. - Aviation:
Morse code is used in aeronautical navigation aids, such as Non-Directional Beacons (NDBs) and VOR stations, which transmit identification codes in Morse. - Emergency Signaling:
The universality of Morse code makes it a valuable tool in emergency situations. The distress signal SOS (● ● ● ▬ ▬ ▬ ● ● ●) is internationally recognized and can be sent using sound, light, or other means.
The Enduring Legacy of Morse Code
Morse code’s simplicity, combined with its effectiveness, has ensured its place in the history of communication. While modern technology has introduced more advanced methods of sending and receiving information, the principles underlying Morse code continue to be relevant. Its legacy is a testament to the ingenuity of early communication pioneers and the enduring value of efficient, adaptable systems.
See Also – Hamster Kombat Daily Cipher 14 August 2024 : Latest Morse Code
See Also – Maximize Your Earnings: Hamster Kombat Daily Combo 12 August 2024 Unlocks 5 Million Coins